Just imagine waking up tomorrow with a website that already has backlinks from major publishers, a stream of visitors, and a solid reputation with search engines. That’s exactly what the right expired domain can offer. So, let’s explore today how to purchase an expired domain name in 2025.
In 2025, when over two billion websites exist on the Internet, thousands of domains expire every day.
Savvy marketers and entrepreneurs are snapping up these aged domains, harnessing their built‑in authority and redirecting their traffic to new or existing ventures.
According to Expired Domains.net, expired domains are a valuable resource for SEO and website building, with thousands becoming available daily. While exact figures fluctuate, several websites and tools track domain expirations and provide lists of available domains. Expired domains with strong backlinks and relevant content can significantly boost a website’s SEO performance.
In this step‑by‑step guide, you’ll learn how to purchase an expired domain name that comes with backlinks and traffic, evaluate its quality, and use it to boost your SEO or launch a new project.
Whether you’re looking for free expired domains, want to automatically buy a domain when it expires, or need a domain expiry checker, this comprehensive resource has everything you need to know.
Continue reading to find much more!
What Are Expired Domains and Why They Matter
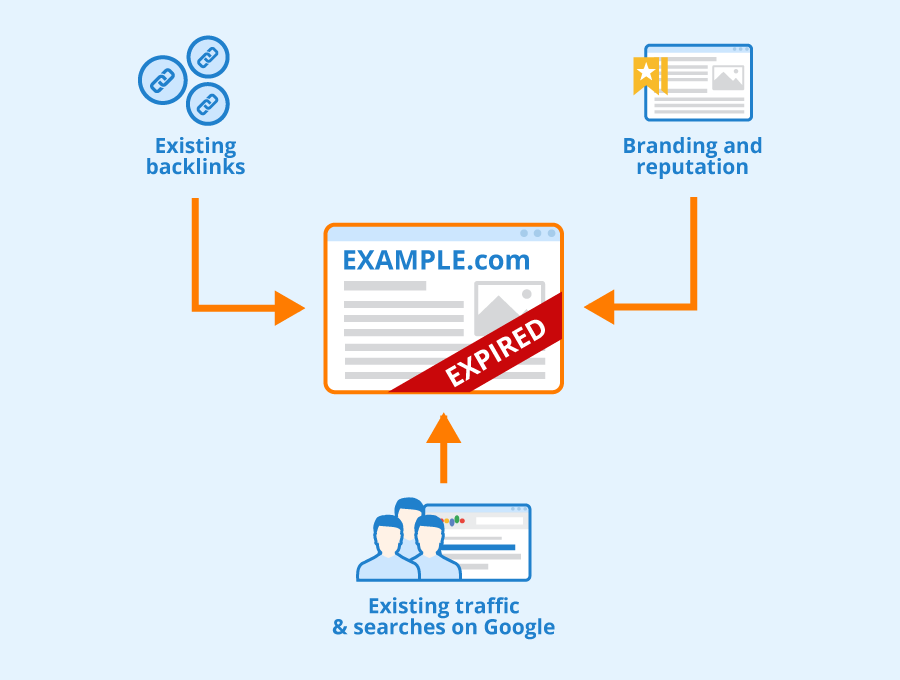
An expired domain is simply a web address that wasn’t renewed by its owner.
Once the renewal date passes, the domain registrar holds it for a grace period and eventually releases it for sale or auction.
These domains often retain existing backlinks, domain authority and even residual traffic from their previous life.
Unlike brand‑new domains, they have a history with Google and other search engines, which can dramatically reduce the time needed to rank a new website.
Dropped vs. Non‑Dropped Domains
During the grace period (around 30–45 days), the original owner can still renew the domain without penalty.
If they don’t, the domain enters the redemption phase, where renewal is possible but costly.
After this, the domain is deleted (“dropped”) and re‑listed for sale or auction.
Dropped domains have an age reset, while non‑dropped domains are those still registered or available in regular markets.
Knowing the difference helps you decide whether to wait for a drop or pursue an auction.
How Domain Expiration Works
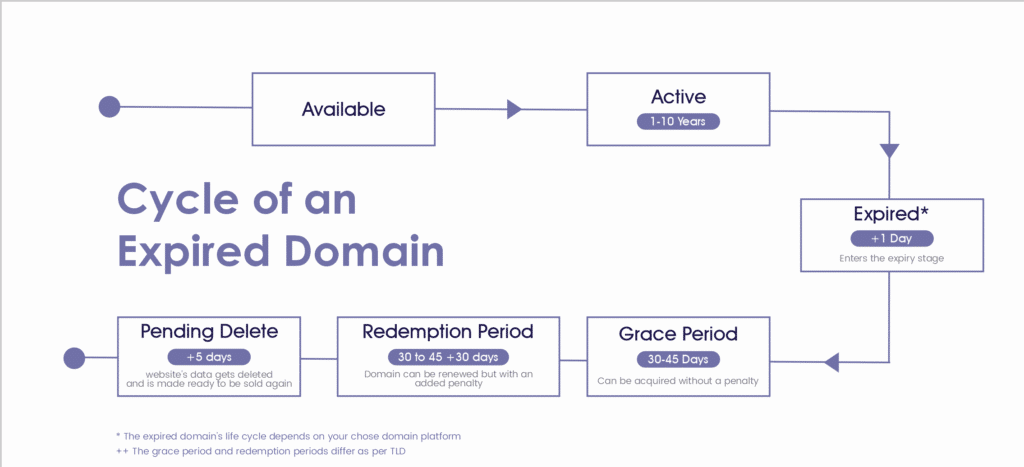
Understanding how domains expire ensures you act at the right time and use tools to monitor prospects.
Expiry Stage: A domain becomes officially “expired” one day after its renewal date.
Grace Period (30–45 days): The owner can renew without penalty. During this time, you can backorder the domain but the original owner still has priority.
Redemption Period (another 30 days): The owner can still renew but must pay a fee. You can place a backorder but there’s no guarantee.
Pending Delete (5 days): The domain is being prepared for deletion. Once deleted, it’s available for auction or general registration.
To monitor a domain’s expiry status, use WHOIS searches or tools such as ExpiredDomains.net, Domain Hunter Gatherer and SpamZilla.
Many registrars provide alert services to automatically buy a domain when it expires or to notify you when it drops. A simple site:example.com search also shows if Google still indexes it.
3 Things Must to Be Considered Before Buying Any Expired Domain
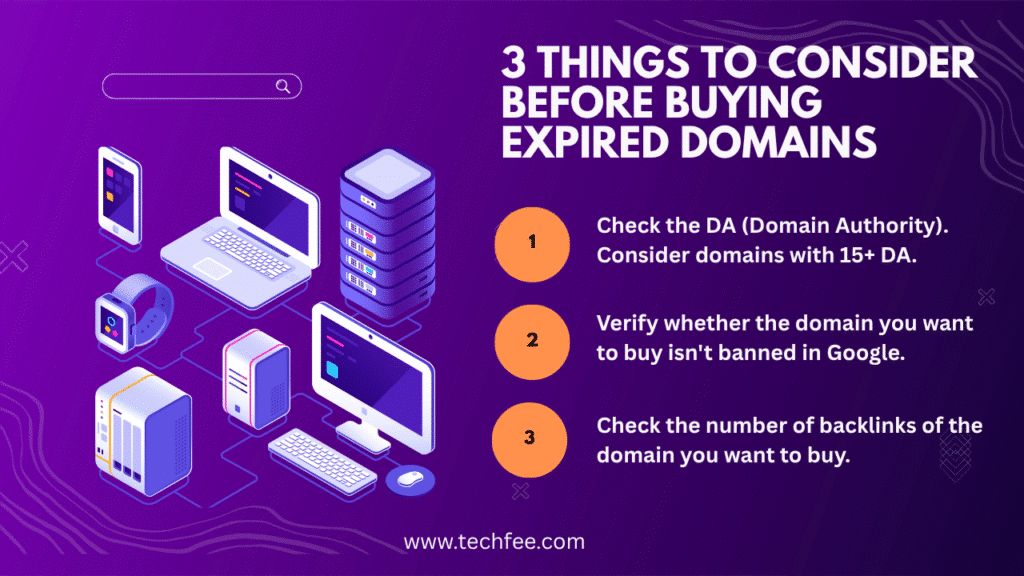
1. Evaluate Domain Authority (DA) and Trust Flow
When considering an expired domain, begin by checking its Domain Authority (DA) and Trust Flow. A DA score above 15 is typically considered decent, while a Trust Flow score over 20 indicates strong credibility and reliability.
Trust Flow is a metric developed by Majestic SEO that reflects how trustworthy a domain is based on the quality of links pointing to it. The higher the score, the more valuable the domain may be for SEO.
2. Check if the Domain is Blacklisted
Before making any purchase, ensure the domain isn’t blacklisted by Google—either from Google Search (de-indexed) or banned from Google AdSense. If a domain has been penalized or blacklisted, it can cause major issues with monetization and SEO visibility.
You can verify blacklist status using tools like IsBanned.com or BannedCheck.
3. Analyze the Backlink Profile
A strong backlink profile is one of the main reasons marketers invest in expired domains. Domains with high-quality backlinks can pass link equity, helping your new site rank faster on search engines.
Use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, or Ubersuggest to check:
The number of referring domains
Quality of backlinks
Anchor text distribution
Link relevance and authority
Avoid domains with spammy or irrelevant backlinks, as they could negatively affect your SEO efforts.
Why Buy Expired Domains? Benefits vs. Drawbacks
Benefits of Buying Expired Domains
Leveraging Existing Backlinks – High‑authority domains often have backlinks from respected websites. Redirecting or rebuilding these domains passes link equity and boosts your SEO.
Built‑In Traffic – Some expired domains still attract visitors. Redirecting them to your new site or rebuilding the original pages can give you instant traffic.
Quicker Rankings – Older domains tend to rank faster than brand‑new ones because search engines already recognise them.
Brand Value and Memorability – Many expired domains are short, memorable or keyword‑rich, making them suitable for branding.
Domain Flipping – Buying undervalued domains and reselling them later can be profitable
Drawbacks and Risks
Spammy Backlink Profiles – Some expired domains were used for spam or link schemes. Buying such a domain could harm your SEO. Always evaluate the backlink profile for unnatural patterns.
Legal Issues – Domains containing trademarked names can be reclaimed by the original brand.
Malware or Phishing History – Check if the domain has been flagged for malicious content using tools like VirusTotal.
Grey‑Hat Strategies – Using expired domains to build Private Blog Networks (PBNs) can lead to penalties if Google detects them.
High Competition and Price – Good domains can attract fierce bidding wars, driving up costs
Market Size & Expiry Volume

Over 10 million domains expired in 2024. This huge volume created a ready supply of aged domains with backlinks and authority for marketers and investors.
More than 150 000 domains expire every day. One backorder provider noted that on a single day in February 2025, over 150 000 domains expired, and tens of thousands expire on any other day.
Data from domain‑list providers shows there can be millions of domains in the “expiring” queue on certain days; for example, DomCop recorded 6 492 922 expiring domains on August 5 2025 and 1 775 678 on August 6. Typical daily counts range from 78 000 to 171 000 expiring domains.
Whois database service Whoxy reports that over 4 million domains are deleted every month. Its calendar of upcoming expirations lists daily drop counts between ~560 000 and 740 000, adding up to around 19.6 million domains expiring over the next month.
There were 368.4 million registered domains globally in early 2025 and .com domains accounted for 157.2 million of them. The aftermarket for domains is projected to reach US$1.17 billion by 2033.
How Investors Acquire and Use Expired Domains
A survey of domain investors found that 41 % acquire their domains via expired‑domain auctions, while 39 % register fresh domains and 20 % buy directly from owners. This underscores the popularity of expired‑domain auctions.
Analysis of 915 expired domains purchased in February 2025 showed that only 3.82 % were used for private‑blog networks (PBNs), just 1 % were repurposed into legitimate websites, 22.9 % were flipped for resale, and 42.2 % were used for money sites or redirects, particularly in the gambling niche. This illustrates that most buyers use expired domains for redirects or resale rather than PBNs.
Over ten million domains expired in 2024, offering a massive reservoir of aged domains for SEO. The steady daily expiry rate means there are always opportunities to acquire domains with authority and backlinks.
Ways to Use Expired Domains (Use Cases)
301 Redirects to Your Main Website – The most common method is to permanently redirect the expired domain to your current site. This passes “link juice” and authority, helping your site rank faster.
Rebuild the Old Website – If the expired domain had significant traffic, you can use the Wayback Machine to restore its content. Once the site regains rankings, either maintain it or redirect it to your main site.
Create a Private Blog Network (PBN) – This involves building multiple sites to link back to your main site. While effective in competitive niches, it is risky and should be approached cautiously.
Flipping or Reselling – Acquire undervalued domains, enhance their value (e.g., by rebuilding or adding content) and sell them later
Branding or Lead Generation – Use the domain for a new business venture or as a “microsite” to capture leads and drive them to your main site.
Where and How to Find Expired Domains

Searching for a high‑authority expired domain can be time‑consuming, but using the right tools and platforms simplifies the process.
Free and Paid Methods
ExpiredDomains.net – Provides comprehensive lists of expired, expiring and dropped domains with search filters. It’s free, but you’ll need to evaluate each domain’s metrics yourself.
Domain Hunter Gatherer – Offers both free and paid options. The free plan lets you search expired domains; the paid version includes advanced metrics and automatic filtering.
SpamZilla – A paid service that analyses spam signals and SEO metrics to help you quickly find quality domains.
Domain Auction Platforms
GoDaddy Auctions – A well‑known platform where users can bid on expired domains. An annual membership (around $4.99) allows you to participate in auctions and list your own domains.
Namecheap Auctions – Another major registrar offering expired domain auctions and backorders.
NameJet – Partnered with multiple registrars, NameJet lets you bid on domains before they drop. It offers filters by price, age, traffic and more.
DropCatch – Specialises in catching recently dropped domains. It uses backorder technology, and the caught domains go into a public auction
SnapNames, Sedo, Afternic – Additional auction sites with varying inventory and pricing.
Fixed‑Price Marketplaces
Odys Global – Curated marketplace with 1,000+ aged domains across 50+ industries. These domains have been filtered and are ready to purchase without bidding wars.
SEO.Domains – Sells top‑level and niche‑specific domains vetted by tools like Ahrefs, Majestic and Moz; buyers can purchase directly without auctions.
DomainCoasters – Focuses on SEO‑valued domains across various industries and highlights trust flow, authority and other metrics.
Flippa – A large marketplace for buying and selling websites and domains. It provides advisory services and a wide range of price points.
Monitoring Newly Expired Domains
Use drop lists and backorder services to track domains “about to drop.”
Set up alerts for keywords or industries so you know when a domain becomes available.
Tools like ExpiredDomains.net can send daily digests of new drops.
How to Evaluate an Expired Domain (Due Diligence Checklist)
Purchasing an expired domain without proper evaluation can backfire. Here’s a thorough checklist:
Indexing Status – Use a
site:domain.comsearch to see if the domain is currently indexed by Google. A domain not indexed may have penalties or no residual SEO value.Historical Usage – Use the Wayback Machine to view past versions of the site. Ensure it wasn’t used for spam, gambling, adult content or other niches unrelated to your intended use.
Niche Relevance – The closer the domain’s previous niche is to your own, the more relevant its backlinks and traffic will be. Relevance is important for Google’s ranking algorithm.
Domain Age & Ownership History – Older domains often carry more authority. Check WHOIS records or services like NameBio to see how many times the domain changed hands and ensure it wasn’t repeatedly dropped.
Backlink Profile – Use tools such as Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz or Majestic to analyse the domain’s Domain Authority/Rating (DA/DR), number of referring domains and inbound/outbound link ratio. Be wary of spammy anchors or unnatural spikes in link activity.
Anchor Text Analysis – Review the anchor texts used in backlinks. If many anchors relate to gambling, porn or pharmaceuticals, proceed with caution.
Traffic & Rankings – Examine historical traffic (via Semrush or Ahrefs) to see if the domain had stable performance. Sudden drops may indicate a manual penalty. Check if the traffic source matches your target audience.
Malware & Phishing History – Use VirusTotal or similar services to ensure the domain hasn’t hosted malicious files or scripts.
Trademark Conflicts – Avoid buying domains that contain trademarked terms, as the original brand could legally reclaim them.
Price Valuation – Use registrar appraisal tools (e.g., GoDaddy’s valuation tool) to get a sense of fair market value. Compare with similar domains on marketplaces.
Taking the time to perform these checks ensures that your expired domain purchase delivers true value rather than costly headaches.
Step‑By‑Step Guide: how to purchase an expired domain name
This section combines all the research above into a clear roadmap for how to buy an expired domain name and incorporate it into your strategy.
1. Define Your Goals and Budget
Decide why you need the domain: 301 redirects, brand building, flipping or PBNs.
Set a maximum spend; auctions can become competitive, so having a limit prevents overbidding.
2. Find Potential Domains
Use free tools (ExpiredDomains.net, Domain Hunter Gatherer) to compile a list.
Browse auctions on GoDaddy, Namecheap, NameJet and others.
Search fixed‑price marketplaces (Odys, SEO.Domains, DomainCoasters) for high‑quality domains.
3. Perform Due Diligence
Apply the evaluation checklist above to each candidate: check indexing, history, niche, backlinks, anchors, traffic, malware and trademarks.
Use multiple SEO tools for cross‑verification. For example, cross‑check domain authority in Moz and Semrush, and use Seobility for a free SEO audit.
Eliminate domains with major red flags.
4. Choose Your Purchasing Method
Auctions: Sign up for auction platforms like GoDaddy Auctions (requires a small membership fee) or NameJet. Place bids within your budget. Understand auction tactics like proxy bidding (automatically raising your bid) and sniping (placing a bid at the last moment).
Backorders: Reserve domains that are about to expire. You’ll be charged only if the domain is successfully caught. Note that multiple parties can backorder the same domain, leading to an auction.
Fixed‑Price Purchase: Browse marketplaces like Odys Global and SEO.Domains for pre‑vetted domains. These are more expensive but eliminate bidding wars and uncertainty.
Registrar Closeouts: Some registrars offer “closeout” domains at fixed prices after auctions end. These can be cheaper but may have fewer high‑quality options.
For cheap expired domains, focus on less popular TLDs or longer names, or hunt through closeouts and less competitive auctions.
5. Place Your Bid or Backorder
Create accounts on multiple platforms to widen your options.
For auctions, set a maximum bid and enable proxy bidding so the system bids on your behalf.
For backorders, ensure your payment method is ready so you don’t miss a catch.
6. Finalise the Purchase
If you win the auction or backorder, complete payment immediately.
The domain is transferred to your account, typically within 7–14 days.
Update the registrant information and enable auto‑renew to avoid losing your new asset
7. Register and Configure
Set up DNS records, hosting and SSL certificates.
If rebuilding, restore content from the Wayback Machine and update it with new, relevant information.
If redirecting, implement 301 redirects carefully to maintain link equity (match pages where possible to preserve relevance).
8. Monitor and Maintain
Track traffic, backlinks and rankings to ensure your new domain performs as expected.
Continue to update content, build new links and engage with your audience.
Optimising and Using Your New Domain
Once you own your expired domain, implement a strategy aligned with your goals.
1. 301 Redirect Implementation
Redirect the entire domain to your main site or specific pages. Redirecting similar content pages preserves topical relevance.
Use a 301 status code, which tells search engines that the page has permanently moved, passing most of the link equity.
2. Rebuilding and Monetising
Use the Wayback Machine to find the site’s previous structure and content.
Replicate the general framework but update the content, design and SEO. This keeps the site relevant and avoids duplicate content issues.
Monetise via ads, affiliate marketing or as a lead‑generation tool.
3. Building a Private Blog Network (PBN) – Advanced and Risky
Host each site separately (different IP addresses, nameservers and CMS themes).
Create unique content for each site.
Link back to your “money site” strategically, blending in other outbound links.
This method carries the risk of manual penalties and is considered grey‑hat.
4. Flipping and Reselling
Improve the domain by rebuilding or redirecting, increasing its traffic and authority.
List it on marketplaces like Flippa or Sedo with documented metrics and a fair appraisal.
5. Blending With Your Marketing Strategy
Use the expired domain for a brand‑extension site or microsite targeting a specific niche or audience.
Deploy it as an independent blog to own more real estate on the SERPs for your main keywords.
Integrate email marketing, social media and content marketing to maximise ROI.
Tips and Best Practices for 2025
Be Patient and Selective – The best domains are rare; don’t rush. Use drop‑list alerts and set Google Alerts for keywords relevant to your industry.
Use Multiple SEO Tools – Cross‑check metrics using Ahrefs, Semrush, Moz, Majestic and Seobility to ensure accuracy.
Avoid Spam and Irrelevance – Even if a domain has high DA/DR, irrelevant anchor texts or a suspicious link profile can harm your site.
Watch for Trademark Issues – Always search trademark databases before purchase.
Invest in High‑Quality Hosting and Security – Use reliable hosting and secure your domain with an SSL certificate.
Build Real Value – Whether redirecting or rebuilding, focus on creating useful content and genuine value for users. Search engines reward relevance and quality.
Conclusion on how to purchase an expired domain name
Purchasing expired domains with strong backlinks and traffic is one of the most effective shortcuts to building online authority in 2025.
With a domain lifecycle spanning grace periods and deletion phases, knowing how to buy a domain when it expires can give you an edge over competitors.
By leveraging existing backlinks and authority, these domains can supercharge your SEO, funnel traffic to your main website, or serve as profitable investments.
However, not every expired domain is a goldmine; due diligence is essential to avoid spam, legal issues or poor performance.
The steps outlined above—finding potential domains, evaluating them using a comprehensive checklist, choosing the right purchase method, and optimising the domain post‑purchase—equip you with a repeatable process for successful expired domain acquisition.
Whether you aim to buy a high‑authority domain, build a Private Blog Network, or simply renew an expired domain name, this guide provides the know‑how to act with confidence.
Ready to start? Begin by creating a shortlist of domains in your niche, apply the evaluation checklist, and jump into your first auction or marketplace. The next high‑authority domain could be just one expired renewal away.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
It depends on the registrar and TLD. Generally, after the 30–45‑day grace period and a 30‑day redemption period, there is a 5‑day pending deletion stage. The domain is then released for registration or auction
If you still own it and it’s within the grace period, simply renew through your registrar. If it’s past redemption, you may need to pay an extra fee. After deletion, anyone can purchase it.
Yes. Many registrars offer backorder services. They attempt to catch the domain the moment it drops, but success depends on competition and registrar policies.
Some lists are free to search, but quality domains almost always require payment—either via auction or fixed price. Avoid “too good to be true” offers; they often involve spammy domains.
Auctions on GoDaddy, Namecheap, NameJet, Sedo and DropCatch are popular. Fixed‑price marketplaces like Odys Global and SEO.Domains offer pre‑vetted aged domains
Perform a WHOIS lookup or use domain monitoring tools that send alerts when a domain enters the expiry stage.
These are domains in the “pending delete” phase or newly dropped. Tools like DropCatch and ExpiredDomains.net provide daily lists.
Yes—if you evaluate them properly. Domains with genuine residual traffic and clean backlinks can provide immediate visitors and SEO gains
Yes, buying expired domains is legal. However, avoid domains with trademark issues to stay clear of legal trouble.
Track domains using tools like ExpiredDomains.net or DomCop, then bid on them via auctions or backorder them through registrars before they are deleted.
Domains can’t be bought permanently. You can register them for up to 10 years at a time, then renew them before expiration to maintain ownership.
Use a reliable platform like GoDaddy Auctions, NameJet, or ODYS. Check the domain’s history, backlinks, spam score, and trademark status before buying.
📣 Enjoyed This Guide? Spread the Word!
If this deep dive into finding and leveraging expired domains helped you, please share it with fellow marketers and entrepreneurs who could benefit too. Your likes and comments not only let us know you value this kind of content, they also help the article reach more people.
💬 Have questions or insights? Leave a comment below—we love hearing about your experiences and suggestions. Your feedback fuels future articles and helps us tailor content to your needs.
📧 Want more actionable digital‑marketing tips? Subscribe to our newsletter to get our latest guides, tools, and exclusive resources delivered straight to your inbox. Join a community of small‑business owners and SEO enthusiasts working to grow smarter in 2025 and beyond.
Thanks for reading and supporting Techfee!